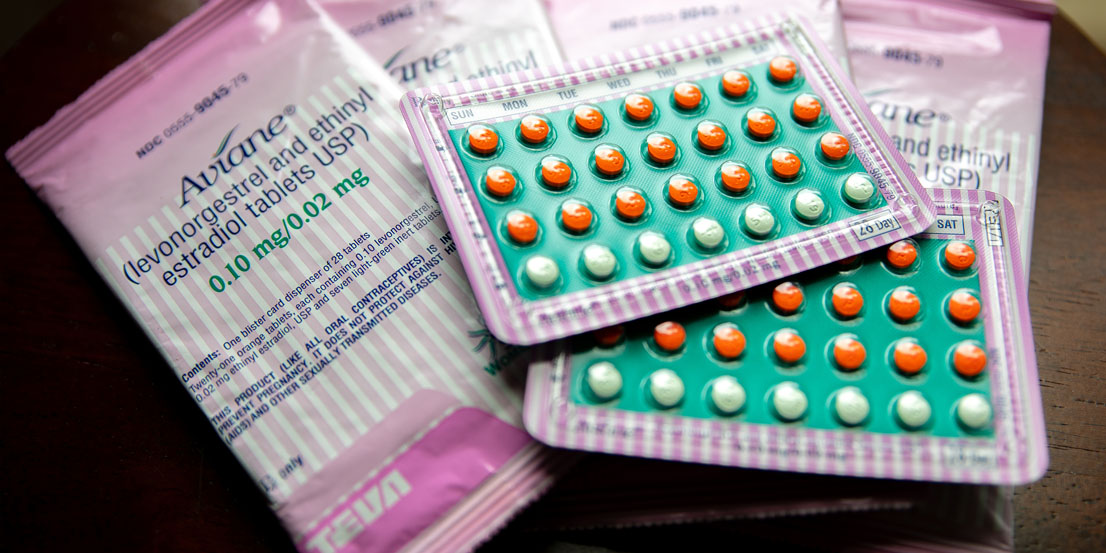
Birth control pills are one of the most popular ways to prevent pregnancy, used by millions worldwide. These tiny pills pack a powerful punch, altering hormone levels in your body to stop ovulation. But that’s not all—they also make other changes that further reduce the chances of pregnancy. In this guide, we’ll break down how these pills work, the different types available, their benefits, possible side effects, and what to consider before choosing the right one for you.
How Do Birth Control Pills Work?
At their core, birth control pills prevent pregnancy by controlling hormones. No ovulation means no egg, and no egg means no fertilization. Simple, right? But there’s more to it. These pills also thicken cervical mucus, making it tough for sperm to get through, and thin the uterine lining, making it harder for a fertilized egg to implant.
The Hormonal Mechanism
Most birth control pills contain synthetic hormones—either a combination of estrogen and progestin or just progestin. Here’s how they work:
- Stopping Ovulation: The pill prevents the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which are essential for ovulation.
- Thickening Cervical Mucus: The mucus in your cervix thickens, creating a barrier that makes it nearly impossible for sperm to reach an egg.
- Thinning the Uterine Lining: Even if an egg does get fertilized, the uterine lining is too thin for implantation.
Types of Birth Control Pills
There are two main types:
1. Combination Pills (Estrogen and Progestin)
These pills contain both estrogen and progestin and come in different forms:
- Monophasic Pills: Each pill has the same hormone dose throughout the cycle.
- Biphasic & Triphasic Pills: Hormone levels vary to mimic natural fluctuations.
- Extended-Cycle Pills: Allow fewer periods by taking active pills continuously for months.
2. Progestin-Only Pills (Mini Pills)
These don’t contain estrogen, making them ideal for those sensitive to it. They mainly work by thickening cervical mucus and sometimes preventing ovulation.
How Effective Are Birth Control Pills?
- Typical Use: About 91% effective due to occasional missed doses.
- Perfect Use: Up to 99% effective when taken correctly every day.
Benefits of Birth Control Pills
Beyond preventing pregnancy, birth control pills offer several perks:
- Regulates Menstrual Cycles: Keeps your cycle predictable.
- Reduces Menstrual Cramps: Lessens period pain.
- Fights Acne: Balances hormones to improve skin.
- Manages PCOS & Endometriosis: Helps control symptoms.
- Lowers Cancer Risk: Long-term use may reduce ovarian and endometrial cancer risks.
Possible Side Effects
While generally safe, some users may experience:
- Nausea & Headaches: Mild and usually temporary.
- Breast Tenderness: A common hormonal side effect.
- Mood Swings: Some people notice changes in mood.
- Spotting Between Periods: Especially in the first few months.
- Blood Clots: A rare but serious risk for certain individuals.
Who Should Avoid Birth Control Pills?
Not everyone should take birth control pills. Those with the following conditions should consult a doctor first:
- History of blood clots or stroke
- Severe migraines with aura
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Liver disease
- Breast cancer history
How to Take Birth Control Pills Correctly
To ensure maximum effectiveness:
- Take It at the Same Time Daily: Keeps hormone levels stable.
- Follow the Prescribed Schedule: Don’t skip pills.
- Missed a Dose? Follow package instructions.
- Use Backup Protection If Needed: If you miss a pill, consider condoms.
Drug Interactions to Watch Out For
Some medications can make birth control pills less effective:
- Certain Antibiotics (e.g., Rifampin)
- Anticonvulsants
- St. John’s Wort
- HIV Medications
Always check with your doctor before starting new medications.
Debunking Common Myths
- “Birth Control Pills Cause Infertility” – False! Fertility usually returns quickly after stopping.
- “You Need a Break from the Pill” – Nope! There’s no medical reason to take a break.
- “Birth Control Causes Weight Gain” – Most studies show no significant long-term weight changes.
Alternative Birth Control Methods
If the pill isn’t for you, consider these options:
- IUDs (Intrauterine Devices)
- Birth Control Patch
- Depo-Provera Shot
- Contraceptive Implants
- Barrier Methods (Condoms, Diaphragms)
Conclusion
Birth control pills are a reliable and convenient way to prevent pregnancy, with added benefits like clearer skin and period regulation. But they’re not for everyone, and side effects vary. The best way to choose the right contraceptive? Talk to your healthcare provider and find what works best for your body and lifestyle.